My own ActiveMQ Artemis Cheat Sheet
🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨
There is an official version of this Cheat Sheet for Red Hat AMQ Broker on the Red Hat Developers portal.
Don’t miss the chance to get it here.
🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨
ActiveMQ Artemis is a high-performance messaging system for highly scalable microservices or asynchronous messaging between different systems.
This cheat sheet includes the most common commands to install, deploy, administrate or operate a messaging system based in ActiveMQ Artemis.
NOTE: ActiveMQ Artemis is the upstream project of Red Hat AMQ 7 Broker, so these commands are also valid for this product.
Enjoy it !!! ![]()
![]()
Cluster Topologies
ActiveMQ Artemis allows defining different of topologies to build simple or complex messaging solutions. The most standard topologies to cover High Availability, scalable and failover scenarios are:
- Symmetric cluster with Replicated journal
- Symmetric cluster with Shared journal
For other cluster topologies, review Cluster Topologies.
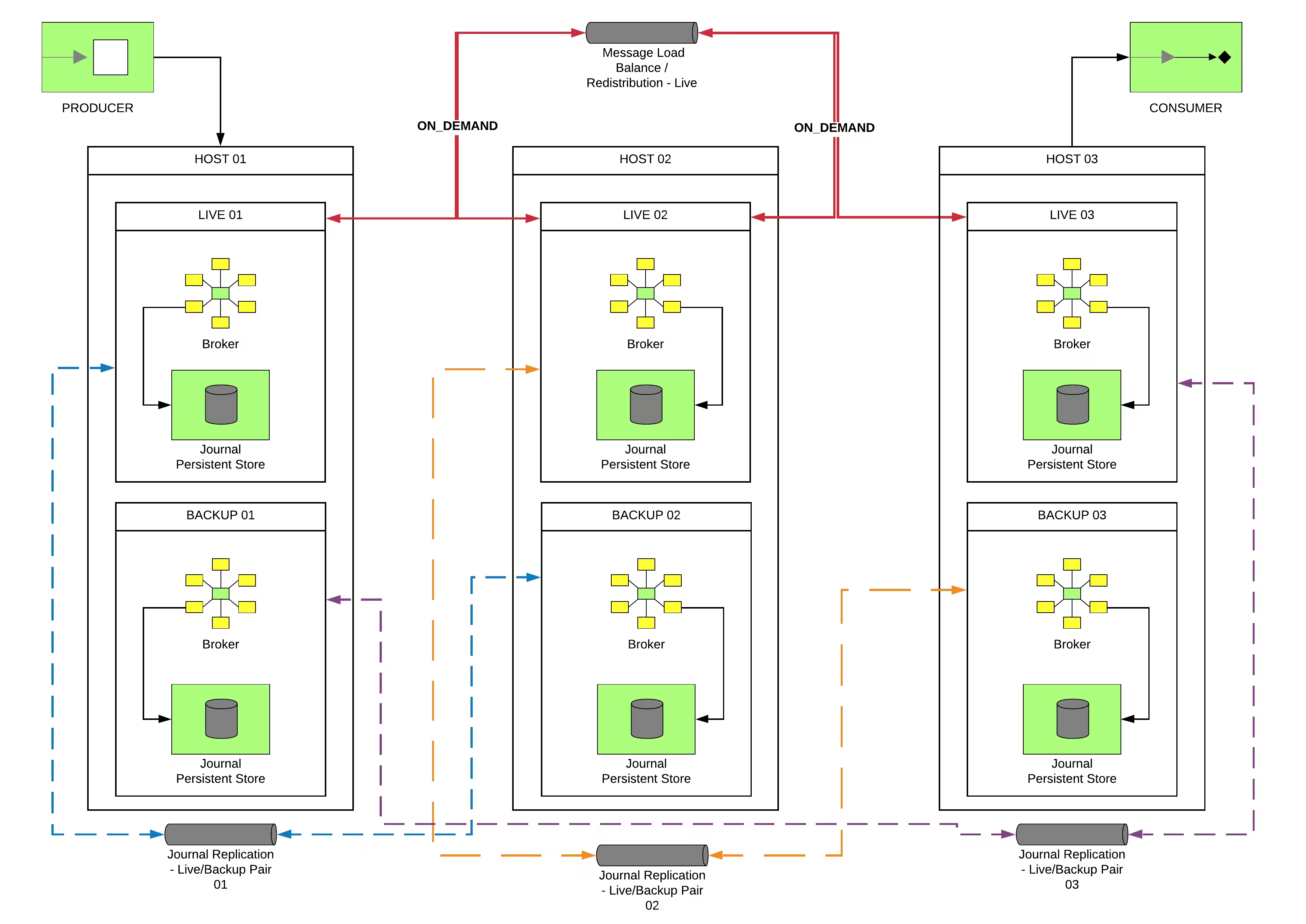
Symmetric Cluster with Replicated Journal
Topology based in:
- Set of live brokers with network journal replication (Symmetric Cluster and High Availability)
- Set of backup brokers for the live brokers (Failover)
This diagram shows us this topology:
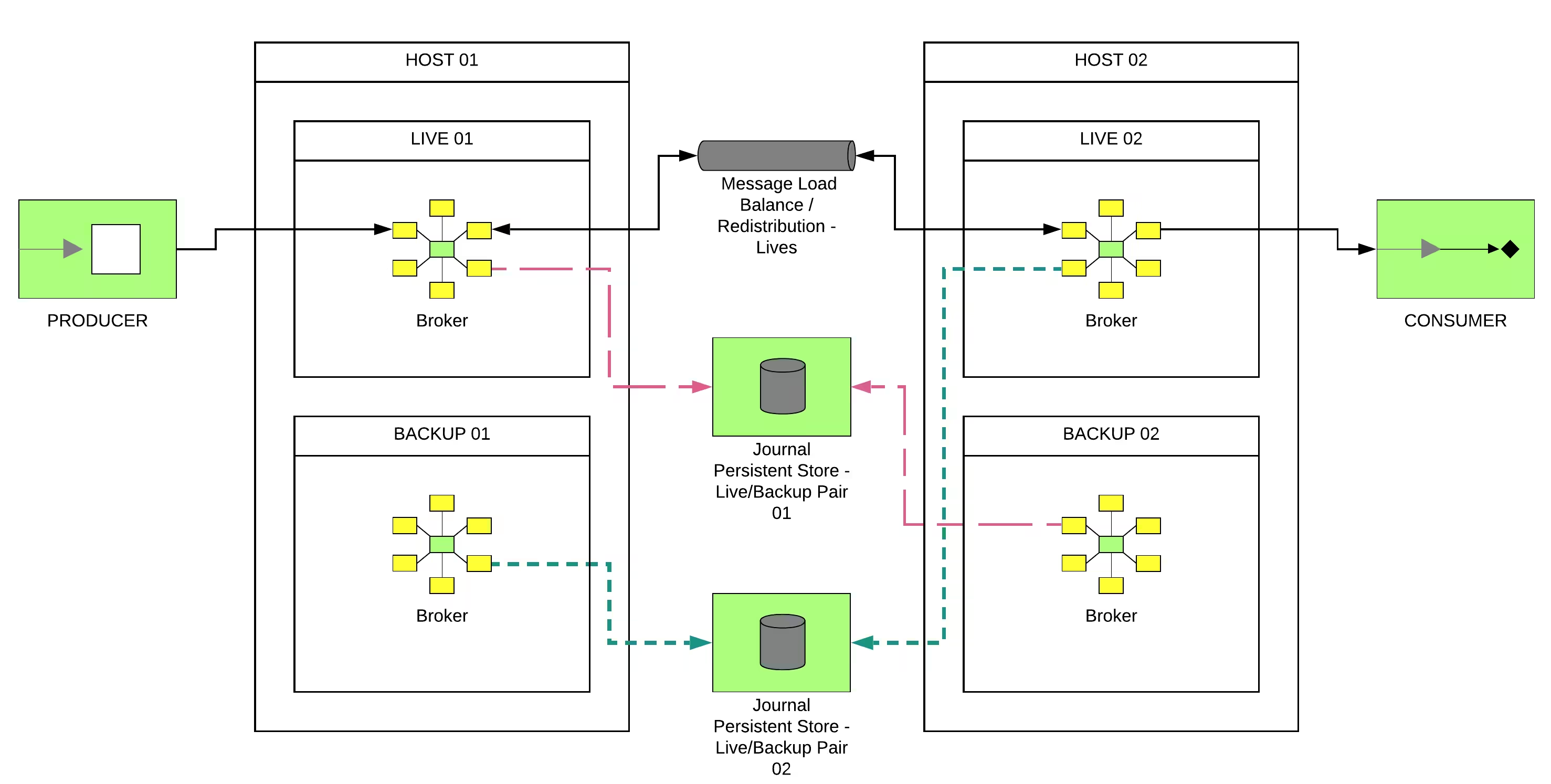
Symmetric Cluster with Shared Journal
Topology based in:
- Set of live brokers with a shared journal (Symmetric Cluster and High Availability)
- Set of backup brokers for the live brokers (Failover)
This diagram shows us this topology:
Deploying Cluster Topologies
Deploying a Symmetric Cluster with Replicated Journal
This command will create a live broker instance in a replicated journal topology:
$ARTEMIS_HOME/bin/artemis create /opt/brokers/live-replicated-broker-XX \
--http-host $HOSTNAME \
--host $HOSTNAME \
--aio \
--clustered \
--cluster-user $ARTEMIS_CLUSTER_USER \
--cluster-password $ARTEMIS_CLUSTER_PASSWORD \
--name live-replicated-broker-XX \
--max-hops 1 \
--user $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_USER \
--password $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--require-login \
--port-offset 0 \
--no-autocreate \
--replicated \
--failover-on-shutdown
This other command will create a backup broker instance for a replicated journal topology:
$ARTEMIS_HOME/bin/artemis create /opt/brokers/backup-replicated-broker-XX \
--http-host $HOSTNAME \
--host $HOSTNAME \
--aio \
--clustered \
--cluster-user $ARTEMIS_CLUSTER_USER \
--cluster-password $ARTEMIS_CLUSTER_PASSWORD \
--name live-replicated-broker-XX \
--max-hops 1 \
--user $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_USER \
--password $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--require-login \
--port-offset 0 \
--no-autocreate \
--replicated \
--failover-on-shutdown \
--slave
By default, ActiveMQ Artemis will use a broadcast network to discover the instances of the topology. The values are identified at runtime of the command and store them in the configuration files.
In case you need to identify the different instances of the topology, the staticCluster property
is needed. This property identifies the static list of other brokers of the topology.
--staticCluster $ARTEMIS_STATIC_CLUSTER_LIST
Samples:
-
ARTEMIS_STATIC_CLUSTER_LIST:
tcp://live-broker-01:61616,...,tcp://live-broker-XX:61616
Deploying a Symmetric Cluster with Shared Journal
This command will create a live broker of a live/backup pair using a shared journal:
$ARTEMIS_HOME/bin/artemis create /opt/brokers/live-broker \
--http-host $HOSTNAME \
--host $HOSTNAME \
--aio \
--clustered \
--cluster-user $ARTEMIS_CLUSTER_USER \
--cluster-password $ARTEMIS_CLUSTER_PASSWORD \
--name live-broker \
--max-hops 1 \
--user $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_USER \
--password $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--require-login \
--port-offset 0 \
--no-autocreate \
--data $ARTEMIS_SHARED_STORAGE_PATH \
--shared-store \
--failover-on-shutdown
For the backup broker instance:
$ARTEMIS_HOME/bin/artemis create /opt/brokers/backup-broker \
--http-host $HOSTNAME \
--host $HOSTNAME \
--aio \
--clustered \
--cluster-user $ARTEMIS_CLUSTER_USER \
--cluster-password $ARTEMIS_CLUSTER_PASSWORD \
--name backup-broker \
--max-hops 1 \
--user $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_USER \
--password $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--require-login \
--port-offset 100 \
--no-autocreate \
--data $ARTEMIS_SHARED_STORAGE_PATH \
--shared-store \
--slave \
--failover-on-shutdown \
Here, the key point is that $ARTEMIS_SHARED_STORAGE_PATH mount a shared storage between both
brokers. It is very common to use a NFSv4 mounted folder.
More details in Persistence.
HA and Failover life cycle
ActiveMQ Artemis includes a failover feature based in the combination of Live and Backup brokers. This feature allows defining an automatic client failover connection.
A client can receive information about all live and backup brokers, so that in the event of a connection failure, it can reconnect to the backup broker. The backup broker then automatically re-creates any sessions and consumers that existed on each connection before failover. This feature saves you from having to hand-code manual reconnection logic in your applications.
When a session is re-created on the backup, it does not have any knowledge of messages already sent or acknowledged. Any in-flight sends or acknowledgements at the time of failover might also be lost. However, even without 100% transparent failover, it is simple to guarantee once and only once delivery, even in the case of failure, by using a combination of duplicate detection and retrying of transactions.
Client connection strings identify a connection string using the Core protocol with the right values to enable the high availability and failover features from the client side. For example:
- Single broker:
tcp://HOSTNAME1:61616?ha=true&reconnectAttempts=10 - Failover connection:
(tcp://HOSTNAME1:616161,tcp://HOSTNAME2:61616)?ha=true&reconnectAttempts=10
Every time a live broker shutdown, the backup instance will be promoted as lived instance to continue the service to producers and consumers, and also to distribute the messages to other members of the topology. The backup instance could delegate again the role to the live instance as soon is is ready. The following definition in the backup instance automate that life cycle:
<ha-policy>
<shared-store>
<slave>
<allow-failback>true</allow-failback>
</slave>
</shared-store>
</ha-policy>
More details in High Availability and Failover.
Message Redistribution
To enable messaging redistribution
between brokers in a cluster, the redistribution-delay property must be enabled to zero in
the <address-setting> in broker.xml file:
<!--default for catch all-->
<address-setting match="#">
<redistribution-delay>0</redistribution-delay>
</address-setting>
Protocols
ActiveMQ Artemis has a pluggable protocol architecture, so that it can easily enable one or more protocols for a network connection. The broker supports the following protocols:
- Core
- AMQP
- MQTT
- OpenWire
- STOMP
- HornetQ
Each protocol could be defined as secure channel (SSL). These channels could be used to define one-way or two-ways to validate the communications from the clients.
More details in Protocols and Interoperability.
Starting a broker
Start a broker instance is very simple:
$ARTEMIS_BROKER_INSTANCE_HOME/bin/artemis run
Or you can run the broker in the background using:
$ARTEMIS_BROKER_INSTANCE_HOME/bin/artemis-service start
Installing as OS service (systemd)
Create a file called artemis.service file in the /etc/systemd/system folder. This file
will have the following content:
[Unit]
Description = ActiveMQ Artemis - Broker
After = syslog.target network.target
[Service]
ExecStart = /opt/brokers/live/bin/artemis run
ExecStop = /opt/brokers/live/bin/artemis stop
User = amq-broker
Group = amq-broker
SuccessExitStatus = 0 143
RestartSec = 60
Restart = on-failure
LimitNOFILE = 102642
[Install]
WantedBy = multi-user.target
To Enable the OS services:
systemctl enable artemis
To start, stop, check the status or restart the OS service:
systemctl (start|stop|status|restart) artemis
Modularizing Broker Configuration
ActiveMQ Artemis supports XML inclusions so the configuration can be broken out into separate files. It is an interesting feature to prevent errors and to ease populating common configuration between clustered brokers.
By default, the etc/broker.xml file declares XInclude XML namespace.
<configuration xmlns="urn:activemq"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XInclude"
...
For example, we could move the addresses tag to an external directory in each host. The live and backup brokers
of the same host will share an addresses.xml configuration file.
❯ cat /opt/brokers/config/addresses.xml
<addresses xmlns="urn:activemq:core">
<address name="DLQ">
<anycast>
<queue name="DLQ" />
</anycast>
</address>
<address name="ExpiryQueue">
<anycast>
<queue name="ExpiryQueue" />
</anycast>
</address>
<!-- Queues and Topics -->
<address name="SampleQueue">
<anycast>
<queue name="SampleQueue" />
</anycast>
</address>
<address name="SampleTopic">
<multicast/>
</address>
</addresses>
This file must be copied in any ActiveMQ Artemis cluster hosts. Finally each broker.xml file
will include it using the xi:include tag:
<xi:include href="/opt/brokers/config/addresses.xml"/>
WARNING: External files are not monitored by the broker so it is needed to refresh or
restart it to take the latest status. touch command could be useful to modify the
timestamp of the broker.xml configuration file:
touch /opt/brokers/live/etc/broker.xml
Automatic Configuration
ActiveMQ Artemis is defined to automatically create an address/queue when a new sender/receiver is
connected. It is a great feature because it allows us to avoid having to manage the address in the
broker.xml file. Also ActiveMQ Artemis also deletes an address/queue when there is
not a sender/receiver connected and there are no messages persisted. This feature is also
great however it includes some extra staff to manage this process.
The following properties in the address-setting section of broker.xml file manages the automatic configuration:
<address-setting match="#">
<auto-create-addresses>false</auto-create-addresses>
<auto-create-queues>false</auto-create-queues>
<auto-create-jms-queues>false</auto-create-jms-queues>
<auto-create-jms-topics>false</auto-create-jms-topics>
<auto-delete-addresses>false</auto-delete-addresses>
<auto-delete-queues>false</auto-delete-queues>
</address-setting>
More details in Automatic Configuration
Producer Command
To send messages to a resource (and easy way to test the broker):
./bin/artemis producer --url '$ARTEMIS_CORE_PROTOCOL_URL' \
--destination $ARTEMIS_RESOURCE \
--user $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_USER --password $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--message-size 1024 --message-count 10 --verbose
Where:
-
ARTEMIS_CORE_PROTOCOL_URL: Identifies a connection string using the Core protocol. Valid values:
- Single broker:
tcp://HOSTNAME1:61616?ha=true&reconnectAttempts=10 - Failover connection:
(tcp://HOSTNAME1:616161,tcp://HOSTNAME2:61616)?ha=true&reconnectAttempts=10
- Single broker:
-
ARTEMIS_RESOURCE: Identifies the resource. Sample values for:
- A Queue:
queue://SampleQueue - A Topic:
topic://SampleTopic
- A Queue:
Consumer Command
To consume messages from a resource (and easy way to test the broker):
./bin/artemis consumer --url '$ARTEMIS_CORE_PROTOCOL_URL' \
--destination $ARTEMIS_RESOURCE \
--user $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_USER --password $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--message-count 10 --verbose
Where:
-
ARTEMIS_CORE_PROTOCOL_URL: Identifies a connection string using the Core protocol. Valid values:
- Single broker:
tcp://HOSTNAME1:61616?ha=true&reconnectAttempts=10 - Failover connection:
(tcp://HOSTNAME1:616161,tcp://HOSTNAME2:61616)?ha=true&reconnectAttempts=10
- Single broker:
-
ARTEMIS_RESOURCE: Identifies the resource. Valid values:
- Queue:
queue://SampleQueue - Topic:
topic://SampleTopic
- Queue:
Durable Subscription Queue
The broker saves messages for any inactive subscribers when a queue is configured as a Durable Subscription. The broker delivers them to the subscribers when they reconnect. Clients are therefore guaranteed to receive each message delivered to the queue after subscribing to it.
A sample definition will be similar to:
<address name="topic">
<multicast>
<queue name="subscription1">
<durable>true</durable>
</queue>
<queue name="subscription2">
<durable>true</durable>
</queue>
</multicast>
</address>
This is a sample definition of a Durable Subscription Queue to be used with the Artemis producer and consumer commands:
<address name="topic.events">
<multicast>
<queue name="c1.Consumer ActiveMQTopic[topic.foo], thread=0">
<durable>true</durable>
</queue>
<queue name="c2.Consumer ActiveMQTopic[topic.foo], thread=0">
<durable>true</durable>
</queue>
</multicast>
</address>
This command produces a number of messages to the topic:
./bin/artemis producer --url tcp://$HOSTNAME:5672 \
--user admin --password admin \
--protocol amqp \
--destination topic://topic.events \
--threads 1 \
--message-count 100 \
--text-size 1024
This command consumes the messages from the c1 subscription:
./bin/artemis consumer --url tcp://$HOSTNAME:5672 \
--user admin --password admin \
--protocol amqp \
--destination topic://topic.events \
--threads 1 \
--message-count 100 \
--durable \
--clientID c1
This other command consumes the messages from the c2 subscription:
./bin/artemis consumer --url tcp://$HOSTNAME:5672 \
--user admin --password admin \
--protocol amqp \
--destination topic://topic.events \
--threads 1 \
--message-count 100 \
--durable \
--clientID c2
NOTE: These queues could be consumed using JMS Message Consumers using Fully Qualified Queue Names (FQQN) as:
String FQQN = "topic::subscription1";
Queue queueDestination session.createQueue(FQQN);
MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(queueDestination);
More details in Addressing Model.
Clustered Message Grouping
This feature allows to process messages with a particular group ID in the same order by the
consumers. Each clustered broker therefore uses a grouping handler to manage the complexity of routing
of grouped messages. Each clustered broker should choose should choose a grouping handler type: Local or Remote.
Local grouping handler broker (only one per cluster topology):
<grouping-handler name="my-grouping-handler">
<type>LOCAL</type>
<address>SampleQueue</address>
<timeout>5000</timeout>
</grouping-handler>
Remote grouping handler broker (the rest of instances of the cluster topology):
<grouping-handler name="my-grouping-handler">
<type>REMOTE</type>
<address>SampleQueue</address>
<timeout>5000</timeout>
</grouping-handler>
To produce grouped messages:
./bin/artemis producer --url $ARTEMIS_CORE_PROTOCOL_URL \
--destination $ARTEMIS_RESOURCE \
--user $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_USER --password $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--message "Sample Grouped Message" \
--message-count 10 \
--group mygroup
To consume grouped messages:
./bin/artemis consumer --url $ARTEMIS_CORE_PROTOCOL_URL \
--destination $ARTEMIS_RESOURCE \
--user $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_USER --password $ARTEMIS_ADMIN_PASSWORD \
--message-count 10 \
--verbose
More details in Clustered Message Grouping
AMQP Secured Connection
Client connection string for AMQP secure protocol:
amqps://HOSTNAME:5671?sslEnabled=true&transport.trustAll=true&transport.verifyHost=false
More details in Configuring Transports
Monitoring
ActiveMQ Artemis includes Jolokia endpoints to execute administrative tasks or query administrative information.
Samples:
- Query the up time of the broker:
❯ curl -u admin:admin 'http://localhost:8161/console/jolokia/read/org.apache.activemq.artemis:broker=!%22live!%22/Uptime' | jq
{
"request": {
"mbean": "org.apache.activemq.artemis:broker=\"live\"",
"attribute": "Uptime",
"type": "read"
},
"value": "1 minute",
"timestamp": 1653917729,
"status": 200
}
- Query to get the total number of messages added:
❯ curl -u admin:admin 'http://localhost:8161/console/jolokia/read/org.apache.activemq.artemis:broker=!%22live!%22/TotalMessagesAdded' | jq
{
"request": {
"mbean": "org.apache.activemq.artemis:broker=\"live\"",
"attribute": "TotalMessagesAdded",
"type": "read"
},
"value": 700,
"timestamp": 1653917823,
"status": 200
}
Performance and Limits
ActiveMQ Artemis manages several resources (descriptors, connections, …) and it is needed to define the OS limits to allow it for the user that runs it.
Review the /etc/security/limits.conf file to add the following definition for this user:
amq-broker soft nofile 65001
amq-broker hard nofile 65001
WARNING: In RHEL 8 this step is no longer needed since nofile defaults have been increased to 1048576 max open files.
ActiveMQ Artemis includes a general server thread pool used for most asynchronous actions on the server side. This pool is defined by default to use only 30 threads and it is very useful to improve the performance.
Definition at broker.xml file:
<thread-pool-max-size>120</thread-pool-max-size>
There are a few things that can go wrong in a production environment (bugs, IO errors, memory issues, …), so ActiveMQ Artemis includes a protection to shut itself down when bad things happen (as a safeguard). This method includes different policies:
-
LOG (default): Log messages into
artemis.logto inform that something is wrong. - HALT (default at broker creation): Stop the messaging process but not the VM.
- SHUTDOWN: Shutdown the VM process.
To check easily if a broker suffered an issue the best practice is to use SHUTDOWN policy. It is
very easy to check if the broker is running or not checking the service or the java process in OS.
Definition at broker.xml file:
<critical-analyzer-policy>SHUTDOWN</critical-analyzer-policy>
More details about performance, tunning and extra features, please review the following references:
Managing users
Add a user:
./bin/artemis user add --url $ARTEMIS_CORE_PROTOCOL_URL \
--user admin --password admin \
--user-command-user user1 \
--user-command-password user1-password1 \
--role role1
Reset a user (change user password and/or role/s):
./bin/artemis user reset --url $ARTEMIS_CORE_PROTOCOL_URL \
--user admin --password admin \
--user-command-user user1 \
--user-command-password user1-password2 \
--role role2,role3
Remove a user:
./bin/artemis user rm --url $ARTEMIS_CORE_PROTOCOL_URL \
--user admin --password admin \
--user-command-user user1
Mask passwords
To mask password to be added in broker.xml file:
$ARTEMIS_HOME/bin/artemis mask $PASSWORD
More details in Generating a masked password.
Getting more Help
ActiveMQ Artemis CLI tool includes an option to get in line help and documentation for each command implemented.
To get detailed information of any kind of command:
./bin/artemis help COMMAND
ActiveMQ Artemis version
This cheat-sheet was tested and verified with the ActiveMQ Artemis 2.18 version.